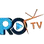As Psychiatry vs Psychology: Understanding the Key Differences takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers with casual formal language style into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
In the following paragraphs, we will delve into the defining disparities between psychiatry and psychology, exploring their distinct approaches to mental health treatment and the educational pathways required for each profession.
Psychiatry vs Psychology: An Overview
Psychiatry and psychology are two distinct fields that focus on mental health and well-being, but they differ in their approach and practice. Psychiatry deals with diagnosing and treating mental illnesses using a medical model, while psychology focuses on understanding human behavior and mental processes through therapy and counseling.
Key Differences
- Psychiatry is a medical specialty that involves prescribing medication and other medical interventions to treat mental illnesses, while psychology uses therapy and counseling to address emotional and behavioral issues.
- Psychiatrists are medical doctors who can prescribe medication, while psychologists usually have a doctoral degree in psychology and cannot prescribe medication.
- Psychiatry often focuses on the biological and neurological aspects of mental health, while psychology emphasizes the role of thoughts, emotions, and behavior in mental well-being.
Approach to Mental Health Treatment
- Psychiatry:Psychiatrists typically use a combination of medication management, psychotherapy, and other medical interventions to treat mental illnesses.
- Psychology:Psychologists employ various therapeutic techniques, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, psychoanalysis, and humanistic therapy, to help individuals overcome emotional and behavioral challenges.
Educational Paths
- Psychiatrist:To become a psychiatrist, one must complete medical school, followed by a residency in psychiatry. This typically takes around 12 years of education and training.
- Psychologist:Psychologists typically earn a doctoral degree in psychology, which involves several years of graduate study and practical training, but they do not attend medical school or complete a medical residency.
Role of Psychiatrists
Psychiatrists are medical doctors who specialize in mental health. They are trained to diagnose and treat a wide range of mental health conditions using a combination of medication, psychotherapy, and other interventions.
Primary Responsibilities of a Psychiatrist
- Conducting psychiatric evaluations to assess mental health symptoms and make a diagnosis.
- Developing treatment plans based on the diagnosis, which may include medication, therapy, or a combination of both.
- Monitoring the progress of patients and adjusting treatment as needed.
- Collaborating with other healthcare professionals, such as psychologists, social workers, and primary care physicians, to provide comprehensive care.
Mental Health Conditions Treated by Psychiatrists
- Depression
- Anxiety disorders
- Bipolar disorder
- Schizophrenia
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
Use of Medication in Psychiatric Treatment
Psychiatrists are licensed to prescribe medication to help manage and alleviate symptoms of mental health conditions. They can prescribe antidepressants, antipsychotics, mood stabilizers, and anti-anxiety medications, among others. The use of medication in psychiatric treatment differs from psychological interventions in that medications directly target chemical imbalances in the brain, while psychological interventions focus on changing thoughts, behaviors, and emotions through therapy.
Role of Psychologists
Psychologists play a crucial role in helping individuals navigate through mental health challenges and improve their overall well-being. They utilize various therapeutic approaches to address psychological issues and provide support to their clients.
Main Duties of a Psychologist
- Conducting psychological assessments to evaluate mental health conditions and determine appropriate treatment plans.
- Providing psychotherapy to individuals, couples, families, or groups to address emotional and behavioral issues.
- Developing and implementing treatment strategies tailored to the specific needs of each client.
- Collaborating with other healthcare professionals to ensure comprehensive care for clients.
Therapeutic Approaches Employed by Psychologists
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): A common approach that focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors.
- Psychodynamic Therapy: Explores unconscious thoughts and past experiences to understand current behaviors and emotions.
- Humanistic Therapy: Emphasizes personal growth, self-awareness, and the importance of the present moment.
- Behavioral Therapy: Focuses on modifying behaviors through reinforcement and conditioning techniques.
Comparison of Psychological Treatment with Psychiatric Treatment
Psychological treatment provided by psychologists tends to focus more on talk therapy and behavioral interventions to address emotional and mental health issues. Psychologists work with clients to explore thoughts, emotions, and behaviors to promote self-awareness and facilitate positive changes. In contrast, psychiatric treatment provided by psychiatrists often involves a combination of medication management and therapy to address mental health conditions.
Psychiatrists are medical doctors who can prescribe medications and may focus more on the biological aspects of mental health disorders.
Treatment Approaches
Psychiatrists and psychologists often collaborate in providing comprehensive mental health care, each bringing unique perspectives and expertise to the table. While psychiatrists focus on the medical aspects of mental health, including prescribing medication and managing biological factors, psychologists emphasize psychotherapy and behavioral interventions to address emotional and cognitive issues.
Collaborative Care
- Psychiatrists and psychologists may work together to develop a holistic treatment plan that combines medication management with therapy to address both the biological and psychological aspects of mental health conditions.
- This collaborative approach can lead to more effective outcomes by addressing the multiple dimensions of mental health issues simultaneously.
- Communication and coordination between the two professionals are crucial to ensure that the treatment plan is cohesive and tailored to the individual’s needs.
Treatment Outcomes
- Research has shown that a combination of psychiatric and psychological interventions can result in better treatment outcomes for certain mental health conditions compared to either approach alone.
- Psychiatric interventions such as medication management can help alleviate symptoms quickly, while psychological interventions like therapy can provide long-term coping strategies and address underlying issues.
- Individual differences, the nature of the mental health condition, and the patient’s preferences all play a role in determining the most effective treatment approach.
Interdisciplinary Approach
- Adopting an interdisciplinary approach in mental health care involves collaboration not only between psychiatrists and psychologists but also with other healthcare professionals such as social workers, occupational therapists, and primary care physicians.
- This approach recognizes the complex nature of mental health issues and the need for a comprehensive treatment plan that considers biological, psychological, social, and environmental factors.
- An interdisciplinary team can provide a range of interventions and support services to address the diverse needs of individuals with mental health conditions, leading to more holistic and personalized care.
End of Discussion
In conclusion, the comparison between psychiatry and psychology sheds light on the intricacies of mental health care, emphasizing the significance of a collaborative and interdisciplinary approach in providing comprehensive treatment. This discussion offers a comprehensive insight into the key variances between these two essential fields.
FAQ Explained
What is the main difference between psychiatry and psychology?
Psychiatry involves diagnosing and treating mental illnesses with medication, while psychology focuses on therapy and counseling to address emotional and behavioral issues.
Do psychiatrists and psychologists work together in treatment plans?
Yes, they often collaborate to provide holistic care, with psychiatrists handling medication management and psychologists offering therapy sessions.
How long does it take to become a psychiatrist versus a psychologist?
Becoming a psychiatrist requires medical school and a psychiatry residency, totaling around 12 years of education, while a psychologist typically completes a doctoral program in psychology, taking about 8-10 years.